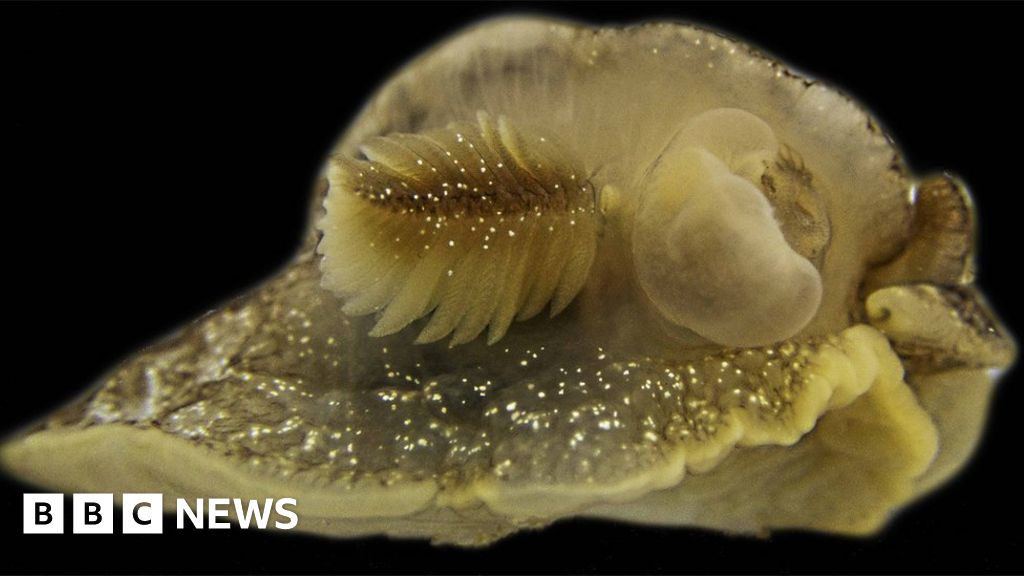
A new species of sea slug has been discovered in UK waters.
It was caught off the south-west of England from a research ship.
The creature has been named Pleurobranchaea Britannica. It belongs to a group found in warmer waters, which could be migrating north due to climate change.
With ocean temperatures at record levels there is concern about the impact on marine life.
Ross Bullimore of the Centre for the Environment, Food and Aquaculture Science (CEFAS) made the serendipitous discovery.
About 100 different sea slugs are found in the seas off Britain and Ireland, but he knew instantly this was something special.
It’s a new type of sea slug. Talk about an anticlimax.
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
A slight variant on a type of known sea slug that’s a little more north than usual, at that.
And there’s a hundred different sea slugs surrounding the country as well. Hard to imagine news that deserved this headline less, really.
Hey, this kind of thing kept Darwin in business for decades.
“Look, a new beetle!!”
These days, though, we know that for every type of beetle there is, there is a species of parasitic wasp that exclusively targets it.
This is the best summary I could come up with:
It belongs to a group found in warmer waters, which could be migrating north due to climate change.
Ross Bullimore of the Centre for the Environment, Food and Aquaculture Science (CEFAS) made the serendipitous discovery.
Despite their diminutive size - growing only to around 5cm (2ins) in length- they are a top predator occupying a key position in the food chain.
Often referred to as an “indicator species”, they can help scientists understand the health of marine ecosystems due to their sensitivity to the impacts of climate change and human pressures.
Members of the group to which the new species belongs - Pleurobranchaea - are usually found in northern Spain, Senegal and throughout the Mediterranean Sea.
Warmer oceans and heatwaves disturb marine species like fish and whales as they move in search of cooler waters, upsetting the food chain.
The original article contains 364 words, the summary contains 139 words. Saved 62%. I’m a bot and I’m open source!